GM9 Glucose Analyser
A premium, world class system, Analox Analysers offer unparalleled analytical performance and versatility to assist the scientific research markets. The Analox GM9 Analyser is an ultra-fast stand alone system for glucose analysis in plasma and other fluids. The system offers exceptional precision and accuracy and is used in a variety of applications and fields.
Contact us to find out how the GM9 can assist with your glucose related testing or for a quote. We also manufacture a range of reagents, kits and standards for use with the GM9 to ensure effective, reliable and reproducible results.
Application Areas
| Area | Example Topics |
| Metabolic Studies |
|
| Biochemical Research |
|
| Studies in Diabetes Mellitus (DM) |
|
| Glucose Clamping |
|
Operation
After calibration with a standard of the selected metabolite, the single injection of sample is all that is needed to obtain a result and prepare the analyser for the next analysis. Sample injection via an accurate positive displacement pipette triggers the complete analytical cycle and a hard-copy result is printed within 25 seconds.
Order Number
Analox-GM9
Analytes
Specification
Instrument Specification
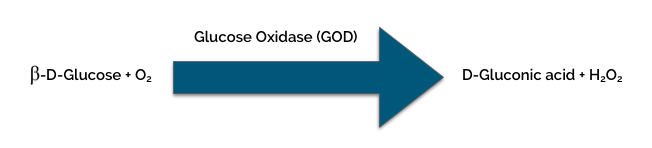
| Method | Enzymatic oxygen-rate |
| Sensor | Clark-type amperometric oxygen electrode |
| Reaction Temp. | 30°C |
| Display | 32 character backlit LCD |
| Printer | Thermal Printer |
| Statistics | Sequential, giving mean, S.D and C.V. |
| Interface | Serial data port |
| Power | 100-250VAC, 50-60Hz, in to Power Supply and 12V , 3.3A DC out |
| Dimensions | 23cm(width) x 29cm(depth) x 15cm(height) |
| Weight | 3.8Kg (Portable, 6Kg) |
Notes:
Example data below, please see GM9 Brochure or Analyte Technical Bulletins for full specifications
Analytical Perfomance
| Precision | Accuracy (Method Comparisons) | Linearity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | C.V. of 1.0% @ 5 mmol/L (plasma) C.V. 1.4 % @ 10 mmol/L (plasma) | i) Method comparison vs Hexokinase: y(Analox) = 0.985x - 0.14 mmol/L, r = 0.999, n = 156 ii) Method comparison vs Beckman; y(Analox) = 1.005x - 0.07 mmol/L, r = 0.999, n = 123 | 30.0 mmol/L (540 mg/dl) for 10µl samples; 50.0 mmol/L (900 mg/dl) for 5µl samples |
Citations
2019
Chronic abdominal vagus stimulation increased brain metabolic connectivity, reduced striatal dopamine transporter and increased mid-brain serotonin transporter in obese miniature pigs
Charles-Henri Malbert, Mickael Genissel, Jean-Louis Divoux, Christine Henry
Journal of Translational Medicine 2019 Mar 12;17(1):78.
C Performance of the SteatoTest, ActiTest, NashTest and FibroTest in a multiethnic cohort of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Bril F, McPhaul MJ, Caulfield MP, et al
Journal of Investigative Medicine Volume 67 pp 303-311
Pharmacologic or genetic activation of SIRT1 attenuates the fat-induced decrease in beta-cell function in vivo
Tejas Desai, Khajag Koulajian, Aleksandar Ivovic, Danna M Breen et al
Nutrition & Diabetes Volume 9, Article number: 11 2019
Carvedilol prevents counterregulatory failure and impaired hypoglycaemia awareness in non-diabetic recurrently hypoglycaemic rats
Rawad Farhat, Gong Su, Anne-Sophie Sejling, Nicholas Knight, Simon J. Fisher, Owen Chan
Diabetologia April 2019, Volume 62, Issue 4, pp 676–686
Effects of short-term sprint interval and moderate-intensity continuous training on liver fat content, lipoprotein profile, and substrate uptake: a randomized trial
Kumail K. Motiani, Anna M. Savolainen, Jussi Toivanen, Jari-Joonas Eskelinen
Journal of Applied Physiology Volume 126, Issue 6, 2019 pp 1756–1796
Physical Activity Associates with Muscle Insulin Sensitivity Postbariatric Surgery
Savolainen AM, Karmi A, Immonen H, et al.
Med Sci Sports Exerc. 51(2) 2019 pp 278–289
Does Weight Status Impact Metabolic Health in Adolescents When Controlling for Physical Fitness?
Stolzman, Stacy C., PT, PhD; Skelton, Joseph, MD; Harkins, April, MT(ASCP), PhD; Hoeger Bement, Marie, PT, PhD
Pediatric Physical Therapy April 2019 Volume 31, Issue 2, pp 134–140
To view the full list of GM9 Citations click here



